This guide will show you how to redirect HTTP to HTTPS using Nginx.
Table of content
Configure Nginx SSL
force HTTP to redirect to HTTPS
force non-www to www
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
OS:Ubuntu 18.04 *64。A Linux server running Nginx
nginx version: nginx/1.14.0 (Ubuntu)
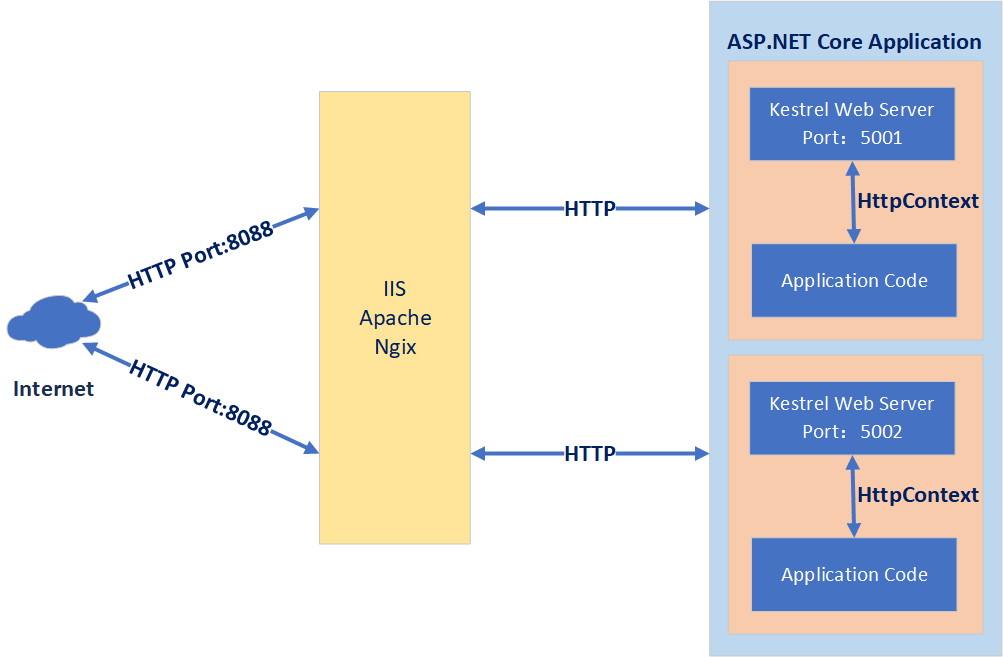
2.转发思路
Browser(https) ---> Nginx (server port 443 ssl)----> HTTP ----> Kestrel
Browser(http) ---> Nginx (server port 80 http)-->redirect 301--> Nginx (server port 443 ssl)----> HTTP ----> Kestrel (force HTTP to redirect to HTTPS )
配置http不带www域名转发
Browser(http://example.com) --->(https://www.example.com) ---> Nginx (server port 443 ssl)----> HTTP ----> Kestrel
配置https不带www域名转发
Browser(https://example.com) --->(https://www.example.com)---> Nginx (server port 443 ssl)----> HTTP ----> Kestrel
To enforce an HTTP to HTTPS redirect, you need to edit the Nginx configuration file.
In most cases, you can locate the file in the /etc/nginx/sites-available directory.
Step 1:create web server port 443 in nginx
vi /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
Create 1 server blocks in the /etc/nginx/sites-enabled file
Step 2:create web server port 80 in nginx
step 3:Redirect HTTP to HTTPS per Site
we recommend to force all your webshop traffic from http:// to https://
server {
listen 80; #监听端口
server_name a.domain.com b.domain.com c.domain.com; #请求域名
return 301 https://$host$request_uri; #重定向至https访问。
}
Step 4:Redirect from www website to non-www website
server {
server_name www.new_company.com;
return 301 $scheme://new_company.com$request_uri;
}other:
Redirect All Sites to HTTPS
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name _;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}or
Let’s analyze the code line by line:
listen 80 default_server - Sets this server block as the default (catch-all) block for all unmatched domains.
server_name _ - _ is an invalid domain name that never matches any real domain name.
return 301 https://$host$request_uri - Redirect the traffic to the corresponding HTTPS server block with status code 301 (Moved Permanently). The $host variable holds the domain name of the request.
For example, if the visitor opens http://example.com/page2 in the browser, Nginx will redirect the request to https://example.com/page2.
Redirect to www
if ($host !~* ^www\.) {
return 301 https://www.$host$request_uri;
}Redirect to non-www
if ($host ~* ^www\.(.*)) {
set $host_without_www $1;
rewrite ^(.*) http://$host_without_www$1 permanent;
}